Boltzmann machines are a type of recurrent stochastic neural network, named after the physicist Ludwig Boltzmann. They are a powerful tool in machine learning, particularly in the realm of generative modeling. This article will delve into the fundamental concepts of Boltzmann Machines, their applications, and the algorithms that drive them.
What is the Boltzmann distribution?
At the heart of Boltzmann Machines lies the Boltzmann distribution. This concept, borrowed from statistical mechanics, defines the probability of a system being in a particular state as a function of the energy of that state. In the context of Boltzmann Machines, states correspond to different configurations of the network’s units, and energy is determined by an energy function specific to the model.
How does a Boltzmann machine work?
A Boltzmann Machine is composed of a set of interconnected binary units that can be either on or off. The connections between these units are symmetric and undirected. The network operates by sampling from a Boltzmann distribution over its possible configurations.
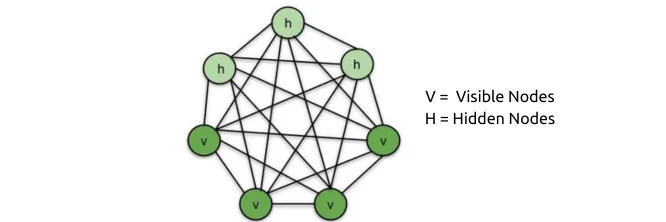
Energy function example for Restricted Boltzmann Machine
A common variant of the Boltzmann Machine is the Restricted Boltzmann Machine (RBM). In an RBM, the units are divided into visible and hidden nodes. The energy function of an RBM can be expressed as:
E = -∑(vi*wi*hj) – ∑(bi*vi) – ∑(cj*hj)
where:
-
vi is the state of the i-th visible unit
-
hj is the state of the j-th hidden unit
-
wi is the weight between the i-th visible unit and the j-th hidden unit
-
bi is the bias of the i-th visible unit
-
cj is the bias of the j-th hidden unit
What is Boltzmann machine used for?
Boltzmann Machines are versatile tools with applications in various fields, including:
-
Generative modeling:
Compartir en: